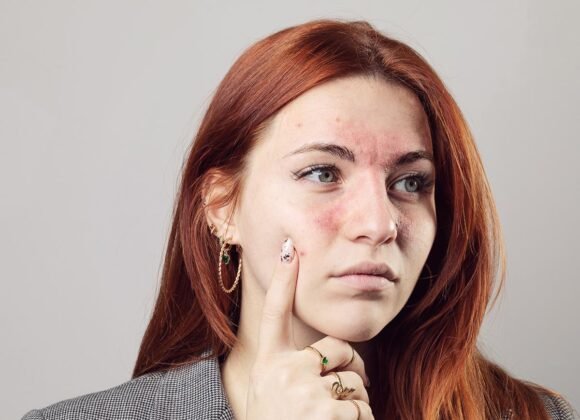
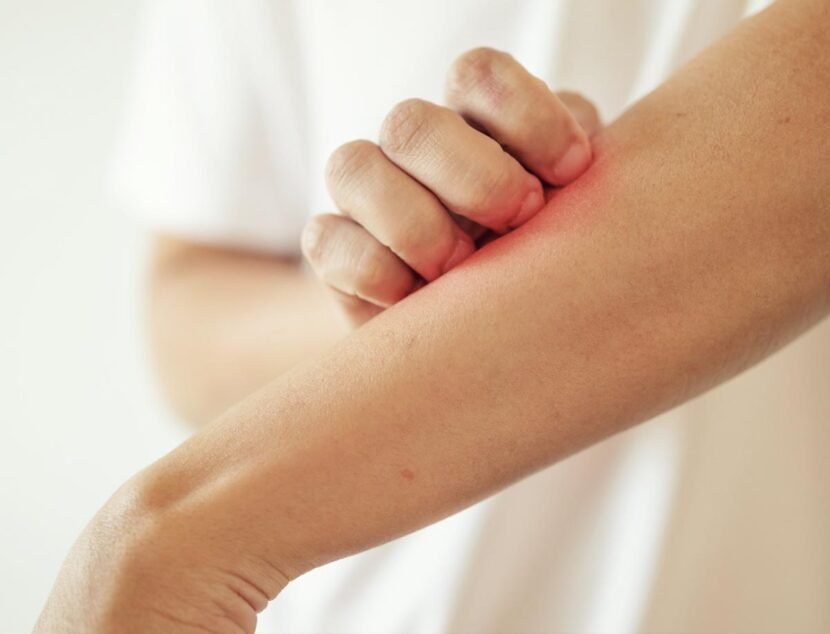
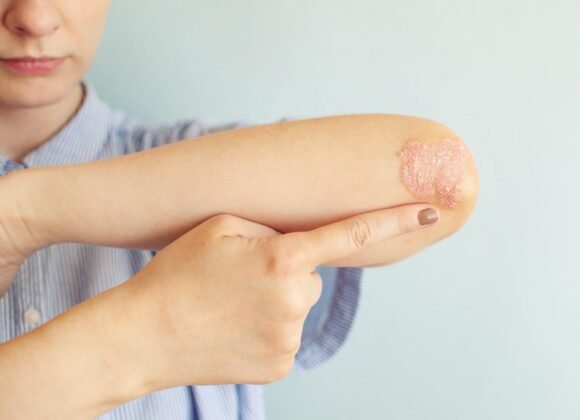
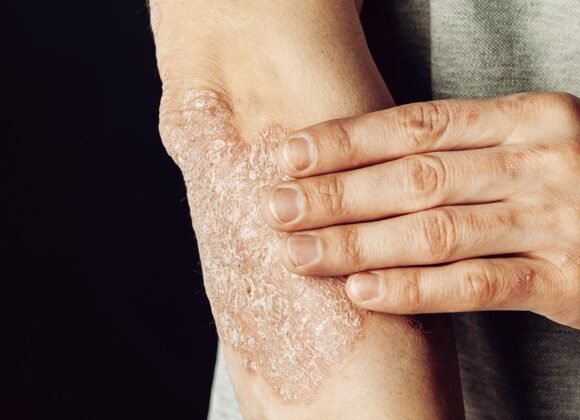
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition affecting millions globally. It manifests as red, itchy, and inflamed skin, causing discomfort and potential cosmetic concerns. Symptoms vary among individuals but typically include dry, scaly skin patches, intense itching, and in severe cases, oozing or crusting.
These symptoms can occur anywhere on the body but are most prevalent on the face, hands, feet, and in the creases of elbows and knees. Various factors can trigger atopic dermatitis flare-ups. Common irritants include soaps, detergents, and certain fabrics, while allergens like pet dander, pollen, and dust mites can also exacerbate the condition.
Additional triggers may include stress, temperature or humidity changes, and specific foods. Identifying and avoiding these triggers is crucial for managing atopic dermatitis and preventing symptom recurrence. It is important to note that atopic dermatitis is not contagious and cannot be transmitted to others.
While living with atopic dermatitis can be challenging, proper understanding and care can lead to effective management. By recognizing the symptoms and triggers associated with this condition, individuals can take proactive measures to minimize flare-ups and improve their overall quality of life.
Key Takeaways
- Atopic dermatitis symptoms include dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, often triggered by irritants, allergens, and stress.
- Eczema symptoms can vary from person to person, but common signs include redness, swelling, and oozing of the skin.
- Triggers of atopic dermatitis can include environmental factors, genetics, immune system dysfunction, and skin barrier defects.
- Managing atopic dermatitis involves gentle skincare, avoiding triggers, using moisturizers, and seeking medical treatment when necessary.
- Care tips for atopic dermatitis include keeping skin moisturized, using mild soaps, wearing soft fabrics, and managing stress to reduce flare-ups.
Eczema Symptoms: Identifying the Signs of Atopic Dermatitis
Common Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
The most common symptom of atopic dermatitis is intense itching, which can be severe enough to interfere with daily activities and disrupt sleep. This itching can lead to scratching, causing the skin to become red, inflamed, and even more itchy.
Long-term Consequences of Atopic Dermatitis
Over time, the cycle of itching and scratching can lead to thickened, leathery skin that is prone to infection. Additionally, dry, scaly patches of skin may appear, which can be red or brownish-gray in color. These patches can occur anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the face, hands, feet, and the bends of the elbows and knees.
Severe Cases and Age-Related Variations
In severe cases, these patches may ooze or crust over, leading to discomfort and embarrassment for those affected. Atopic dermatitis can affect people of all ages, from infants to adults. In infants, the rash often appears on the cheeks, scalp, and other parts of the body. In children and adults, the rash is more commonly found on the elbows and knees.
Causes of Eczema: Uncovering the Triggers of Atopic Dermatitis
Uncovering the triggers of atopic dermatitis is an important part of managing the condition effectively. While the exact cause of atopic dermatitis is not fully understood, it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. People with a family history of atopic dermatitis, asthma, or hay fever are more likely to develop the condition themselves.
Additionally, certain environmental factors such as exposure to allergens or irritants can trigger flare-ups in those who are predisposed to atopic dermatitis. Common triggers for atopic dermatitis include irritants such as soaps, detergents, and certain fabrics. Allergens like pet dander, pollen, and dust mites can also trigger flare-ups.
Other triggers can include stress, changes in temperature or humidity, and certain foods. Identifying these triggers and taking steps to avoid them is an important part of managing atopic dermatitis effectively. It is also important to note that atopic dermatitis is not caused by poor hygiene or an allergic reaction to a specific substance.
While certain substances can trigger flare-ups in those who are predisposed to atopic dermatitis, they are not the underlying cause of the condition. By understanding the causes and triggers of atopic dermatitis, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize flare-ups and improve their quality of life.
How to Treat Eczema: Managing Atopic Dermatitis with Care Tips
Managing atopic dermatitis effectively requires a combination of self-care strategies and medical treatment. One of the most important aspects of managing atopic dermatitis is keeping the skin moisturized. Using a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer regularly can help to soothe dry, itchy skin and prevent flare-ups.
It is also important to avoid harsh soaps and detergents that can strip the skin of its natural oils and exacerbate symptoms. In addition to moisturizing the skin, it is important to avoid scratching as much as possible. This can be challenging, especially when the itching is intense, but scratching can further irritate the skin and lead to infection.
Keeping fingernails short and wearing gloves at night can help to prevent scratching while sleeping. For those with more severe symptoms, medical treatment may be necessary. This can include prescription-strength corticosteroid creams or ointments to reduce inflammation and itching.
In some cases, oral medications or phototherapy (light therapy) may be recommended by a healthcare professional. By following these care tips and seeking appropriate medical treatment when necessary, individuals with atopic dermatitis can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Care Tips for Atopic Dermatitis: Ways to Soothe and Manage Symptoms
Soothing and managing the symptoms of atopic dermatitis requires a comprehensive approach that includes self-care strategies and lifestyle adjustments. In addition to keeping the skin moisturized and avoiding scratching, there are several other care tips that can help to soothe and manage symptoms. One important care tip is to avoid known triggers as much as possible.
This may involve making changes to your home environment, such as using hypoallergenic bedding or air purifiers to reduce exposure to allergens like dust mites or pet dander. It may also involve making changes to your diet if certain foods trigger flare-ups. Another care tip is to dress in loose-fitting, breathable clothing made from soft fabrics like cotton.
This can help to reduce irritation and itching caused by friction from clothing. It is also important to manage stress effectively, as stress can be a trigger for atopic dermatitis flare-ups. Engaging in relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises or yoga can help to reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being.
By incorporating these care tips into your daily routine, you can help to soothe and manage the symptoms of atopic dermatitis effectively.
Lifestyle Changes for Atopic Dermatitis: Creating a Skin-Friendly Environment
Modifying Your Home Environment
Creating a skin-friendly environment is crucial for effectively managing atopic dermatitis. This involves making changes to your home environment to reduce exposure to known triggers such as allergens or irritants. Using hypoallergenic bedding, air purifiers, and vacuum cleaners with HEPA filters can help reduce exposure to dust mites and pet dander.
Adapting Your Cleaning Routine
In addition to modifying your home environment, it’s essential to adjust your cleaning routine. Using gentle, fragrance-free cleaning products that won’t irritate the skin can help create a skin-friendly environment. This simple change can make a significant difference in managing atopic dermatitis.
Lifestyle Changes for a Skin-Friendly Environment
Several lifestyle changes can also help create a skin-friendly environment for those with atopic dermatitis. One important change is to avoid hot showers or baths, as hot water can strip the skin of its natural oils and exacerbate symptoms. Instead, opt for lukewarm water and limit bathing time to 10-15 minutes. Additionally, be mindful of your clothing choices, avoiding tight-fitting clothing made from synthetic fabrics that can trap sweat and irritate the skin. Opt for loose-fitting clothing made from soft fabrics like cotton that won’t cause friction or irritation. By making these lifestyle changes and creating a skin-friendly environment, individuals with atopic dermatitis can minimize flare-ups and improve their overall quality of life.
Seeking Professional Help: When to Consult a Dermatologist for Atopic Dermatitis
While self-care strategies and lifestyle adjustments can help to manage mild cases of atopic dermatitis effectively, there are times when it is necessary to seek professional help from a dermatologist. If you are experiencing severe or persistent symptoms that are not responding to self-care strategies, it may be time to consult a healthcare professional. A dermatologist can provide a thorough evaluation of your skin and symptoms and recommend appropriate medical treatment based on your individual needs.
This may include prescription-strength corticosteroid creams or ointments to reduce inflammation and itching. In some cases, oral medications or phototherapy (light therapy) may be recommended. In addition to medical treatment, a dermatologist can provide valuable guidance on how to manage your condition effectively and prevent flare-ups in the future.
They can also help you identify specific triggers for your atopic dermatitis and provide recommendations for avoiding them. By seeking professional help when necessary, individuals with atopic dermatitis can receive the care and support they need to effectively manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
FAQs
What are the common symptoms of atopic dermatitis?
Common symptoms of atopic dermatitis include dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, as well as red or brownish-gray patches. In severe cases, the skin may also develop blisters and become crusty and scaly.
What causes atopic dermatitis?
The exact cause of atopic dermatitis is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Triggers for atopic dermatitis can include certain foods, allergens, stress, and irritants like soaps and detergents.
How is atopic dermatitis typically treated?
Treatment for atopic dermatitis often involves a combination of moisturizing creams or ointments, topical corticosteroids, antihistamines, and in some cases, immunosuppressant medications. Avoiding triggers and maintaining a good skincare routine are also important for managing the condition.
Are there any lifestyle changes that can help manage atopic dermatitis?
Lifestyle changes that can help manage atopic dermatitis include avoiding known triggers, using mild soaps and detergents, wearing soft, breathable fabrics, and maintaining a consistent skincare routine. Managing stress and maintaining a healthy diet may also help improve symptoms.
When should someone with atopic dermatitis seek medical attention?
It is important for individuals with atopic dermatitis to seek medical attention if their symptoms worsen, if they develop signs of infection such as pus or yellow crusts on the skin, or if their condition significantly impacts their quality of life. A healthcare professional can provide guidance on managing the condition and may prescribe additional treatments if needed.