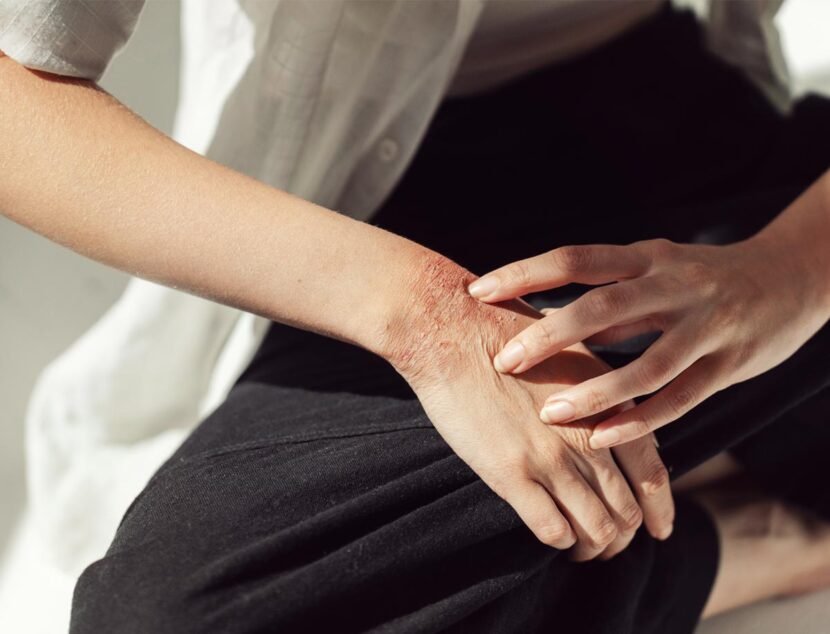
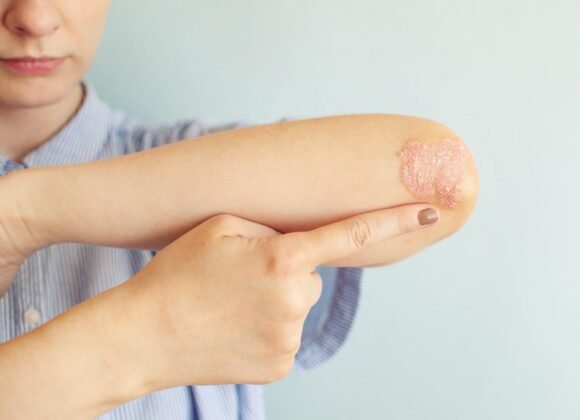
Stasis dermatitis, also called venous eczema, is a skin condition caused by poor circulation in the lower legs. This results in fluid buildup and increased pressure in the veins, leading to symptoms such as redness, swelling, itching, and skin discoloration. The affected skin may become dry, flaky, and cracked, increasing the risk of infection.
Stasis dermatitis is typically a chronic condition that requires ongoing management to prevent flare-ups and complications. The primary cause of stasis dermatitis is venous insufficiency, which occurs when the leg vein valves are weakened or damaged, impeding blood flow back to the heart. Factors contributing to this condition include age, obesity, pregnancy, and a sedentary lifestyle.
Other risk factors may include a history of blood clots, varicose veins, or heart failure. While stasis dermatitis is more prevalent in adults over 50, it can affect individuals of any age. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking prompt treatment is crucial for preventing complications and improving quality of life.
Key Takeaways
- Stasis dermatitis is a skin condition caused by poor circulation in the legs, leading to symptoms such as swelling, redness, and itching.
- Eczema symptoms in stasis dermatitis include dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, often appearing on the lower legs and ankles.
- Poor circulation contributes to stasis dermatitis by causing blood to pool in the legs, leading to increased pressure and fluid leakage into the surrounding tissues.
- Treating stasis dermatitis involves managing symptoms with moisturizers, compression stockings, and elevating the legs, as well as addressing the underlying circulation issues.
- Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, avoiding prolonged sitting or standing, and maintaining a healthy weight can help improve circulation and manage stasis dermatitis.
Recognizing Eczema Symptoms in Stasis Dermatitis
Symptoms of Stasis Dermatitis
The skin may appear red or discolored, and it may feel warm to the touch. Itching is a common symptom of eczema and can be particularly bothersome in stasis dermatitis. The skin may also become dry, flaky, and cracked, making it more susceptible to infection.
Complications of Stasis Dermatitis
In addition to these symptoms, individuals with stasis dermatitis may also experience swelling in the lower legs and ankles due to fluid buildup. This can lead to a feeling of heaviness or tightness in the legs. Over time, the skin may become thickened and discolored, taking on a brownish or reddish hue.
Importance of Early Intervention
It is important to recognize these symptoms and seek medical attention if you suspect you may have stasis dermatitis. Early intervention can help prevent complications and improve the overall management of the condition.
How Poor Circulation Contributes to Stasis Dermatitis
Poor circulation is a key factor in the development of stasis dermatitis. When blood flow is compromised, particularly in the lower legs and ankles, it can lead to a buildup of fluid and pressure in the veins. This can cause the surrounding tissues to become inflamed and irritated, leading to the characteristic symptoms of stasis dermatitis.
In addition to fluid buildup, poor circulation can also impair the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the skin, leading to dryness, flakiness, and an increased risk of infection. There are several factors that can contribute to poor circulation, including obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes and heart disease. Aging can also play a role in the development of poor circulation, as blood vessels may become less elastic and less efficient at pumping blood back to the heart.
It is important to address these underlying causes of poor circulation in order to effectively manage stasis dermatitis. Lifestyle changes and medical treatments can help improve circulation and reduce the risk of flare-ups.
Treating Eczema and Stasis Dermatitis
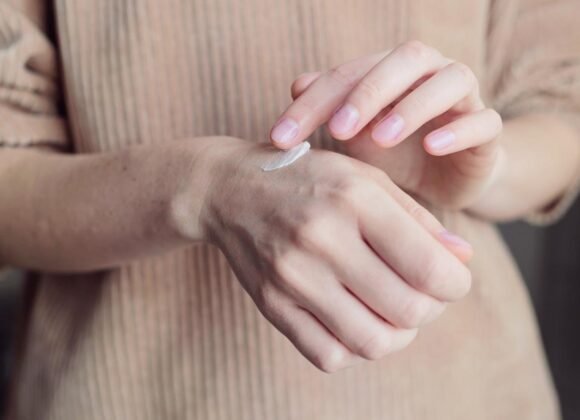
The treatment of eczema and stasis dermatitis typically involves a combination of approaches aimed at managing symptoms and addressing underlying causes. Topical treatments such as moisturizers and corticosteroid creams can help relieve itching and inflammation, while also helping to repair the skin barrier. In some cases, wet dressings or bandages may be used to help soothe and protect the affected skin.
It is important to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for using these treatments to ensure their effectiveness and safety. In addition to topical treatments, lifestyle changes can play a key role in managing eczema and stasis dermatitis. Elevating the legs when sitting or lying down can help reduce swelling and improve circulation.
Regular exercise can also help improve blood flow and overall cardiovascular health. Wearing compression stockings or socks can provide support for the veins and help prevent fluid buildup in the legs. It is important to work with your healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses your individual needs and concerns.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve Circulation and Manage Stasis Dermatitis
Making lifestyle changes can be an effective way to improve circulation and manage stasis dermatitis. Regular exercise, particularly activities that promote leg movement such as walking or cycling, can help improve blood flow and overall cardiovascular health. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can also reduce the strain on the circulatory system and lower the risk of developing stasis dermatitis.
Avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing can help prevent fluid buildup in the legs. Elevating the legs when sitting or lying down can help reduce swelling and improve circulation. This can be particularly beneficial after long periods of standing or sitting.
Wearing compression stockings or socks can provide support for the veins and help prevent fluid buildup in the legs. These garments are designed to apply pressure to the legs, promoting better blood flow back to the heart. It is important to work with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate type of compression garment for your individual needs.
Medical Treatments for Stasis Dermatitis
Topical Treatments
In addition to lifestyle changes, topical treatments such as moisturizers and corticosteroid creams can help relieve itching and inflammation, while also helping to repair the skin barrier. In some cases, wet dressings or bandages may be used to help soothe and protect the affected skin.
Oral Medications and Injections
In more severe cases of stasis dermatitis, oral medications or injections may be prescribed to help reduce inflammation and improve circulation. These medications may include diuretics to reduce fluid buildup, antihistamines to relieve itching, or antibiotics to treat infections.
Surgical Interventions
In some cases, surgical interventions such as vein stripping or laser therapy may be recommended to address underlying venous insufficiency.
Working with Your Healthcare Provider
It is important to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for using these treatments to ensure their effectiveness and safety. It is also important to work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your individual needs.
Preventing Stasis Dermatitis and Eczema Flare-ups
Preventing flare-ups of stasis dermatitis and eczema involves managing underlying causes such as poor circulation and skin barrier dysfunction. This may include making lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing. Elevating the legs when sitting or lying down can help reduce swelling and improve circulation.
Wearing compression stockings or socks can provide support for the veins and help prevent fluid buildup in the legs. In addition to lifestyle changes, it is important to take steps to protect the skin from irritants and allergens that can trigger eczema flare-ups. This may include using gentle cleansers and moisturizers, avoiding harsh soaps and detergents, and wearing protective clothing when working with chemicals or other potential irritants.
It is also important to avoid scratching or rubbing the affected skin, as this can further irritate the skin and lead to infection. Working with your healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses your individual needs can help prevent flare-ups and improve overall management of stasis dermatitis and eczema.
FAQs
What is stasis dermatitis?
Stasis dermatitis is a skin condition that occurs due to poor circulation in the legs, leading to swelling, redness, and irritation of the skin.
What are the symptoms of stasis dermatitis?
Symptoms of stasis dermatitis include swelling in the legs, red or discolored skin, itching, pain, and the development of open sores or ulcers.
What causes poor circulation in the legs?
Poor circulation in the legs, which can lead to stasis dermatitis, can be caused by conditions such as varicose veins, obesity, blood clots, or heart failure.
How is stasis dermatitis diagnosed?
Stasis dermatitis is typically diagnosed through a physical examination of the affected skin, along with a review of the patient’s medical history and any underlying conditions that may contribute to poor circulation.
What are the treatment options for stasis dermatitis?
Treatment for stasis dermatitis may include compression stockings to improve circulation, topical ointments or creams to reduce inflammation and itching, and in severe cases, surgery to address underlying circulation issues.
Can stasis dermatitis be prevented?
Preventative measures for stasis dermatitis include maintaining a healthy weight, staying physically active, avoiding prolonged periods of standing or sitting, and managing any underlying conditions that may contribute to poor circulation.